To the inexperienced user, the Domain Name System (DNS) can seem intricate and complicated. However, understanding the core ideas behind DNS can simplify this seemingly complex system. DNS’s primary purpose is to convert domain names into IP addresses, akin to turning a street address into a physical location.
What is DNS?
To the inexperienced user, the Domain Name System (DNS) can seem very intricate and complicated. While it can in some cases be complex, DNS problems can be easily diagnosed once you understand the basic core ideas behind it.

What does DNS do?
DNS has one primary purpose online: Turn names into numbers. The numbers are IP addresses, which function just like the numbers in your home address. Mail that is delivered to your home is physically delivered by a mail carrier who knows where your address is located. DNS is like a mail carrier, taking domain names and turning them into unique addresses that allow messages to be sent back and forth across the internet.
Specifically, DNS turns names like xeonbd.com, google.com, yahoo.com, etc into the IP addresses of the servers that host the website.
How does DNS do its job?
A short explanation of the DNS process:
- You purchase a domain at a Registrar (OnlineNic, Directi, GoDaddy, Enom, etc).
- The Registar lets the world know what nameservers have your domain’s DNS.
- The Nameservers house your domain’s DNS. When someone wants to connect to your domain the nameservers turn the domain name into an IP address and send the result to the visitor’s computer.
- The visitor’s computer receives the IP address answer from the nameservers and opens a connection to the web server at that address, requesting the web page.
- The web server responds and fulfills the request, transmitting the web page to the visitor’s computer.
Please note that this overview does not include local resolvers for the sake of making general DNS concepts easier to understand.
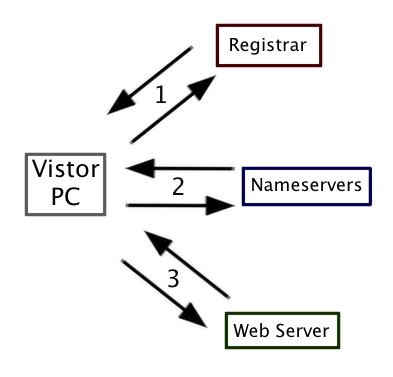
- The Visitor PC requests nameserver information from the registrar.
- The nameservers turn the domain name into an IP address and send it to the Visitor.
- The Visitor’s PC connects to the web server IP and requests the domain’s page, which is then sent back to the Visitor’s PC.
In short, by converting domain names into IP addresses, DNS makes internet communication seamless and efficient.




